Introduction:
Symptoms of Scabies in Humans- Are you experiencing persistent itching and an unrelenting urge to scratch? If so, you may be dealing with scabies – a common skin condition caused by tiny mites burrowing into the top layer of your skin. Scabies can be uncomfortable and highly contagious, but don’t worry!
This blog post will go into information about symptoms of scabies in humans, from its early signs to its impact on mental health. By understanding these symptoms, You will have improved readiness to identify and seek appropriate treatment for this pesky condition. So, let’s dive in and uncover the telltale signs of scabies!
What is Scabies?
Sarcoptes scabiei, a tiny mite, is the cause of the highly infectious skin disorder scabies. These small parasites burrow into the outer layer of your skin, where they lay eggs and cause intense itching.
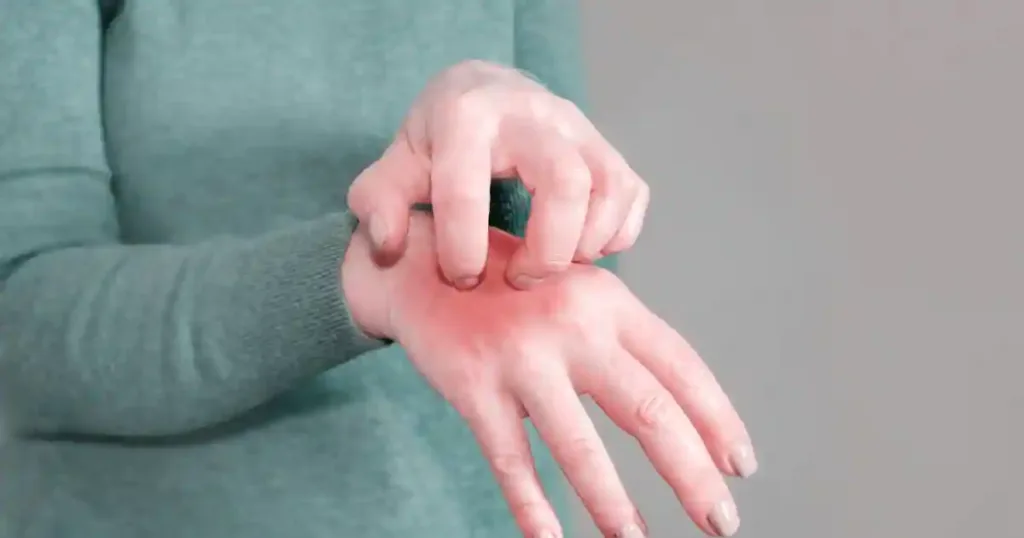
The mites are typically transmitted through close physical contact with an infected individual, such as holding hands or sexual activity. However, it’s also possible to contract scabies by sharing personal items like bedding or clothing with someone who has the condition.
– First Signs
Once scabies have exposed you, symptoms may take several weeks to appear. The first signs often include small red bumps or blisters on the skin, accompanied by severe itching that worsens at night. The itchiness can be so relentless that it disrupts sleep and affects daily activities.
Common areas where scabies rashes occur include between fingers, wrists, elbows, armpits, waistline, genitals in males and breasts in females. In infants and young children, the scalp may also be affected.
– Bacterial Infections
Scabies can lead to complications such as bacterial infections due to excessive scratching if left untreated. You must get medical help as soon as you think you may have scabies.
Remember that early identification and treatment are critical when dealing with this issue!
How Do Scabies Spread?
Sarcoptes scabiei, a tiny mite, is the cause of the infectious skin condition called scabies. These minuscule creatures burrow into the top layer of the skin, laying eggs and causing intense itching and discomfort. But how do scabies spread from person to person?
The primary mode of transmission for scabies is through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual. It can occur during hugging, holding hands, or sexual contact. However, it’s important to note that scabies can also be spread indirectly through infested bedding, clothing, or furniture.
The mites are highly resilient and can survive up to 72 hours outside the human body. Therefore, simply coming into contact with contaminated surfaces can put you at risk of contracting scabies.
It’s worth mentioning that scabies outbreaks often occur in crowded environments such as nursing homes, prisons, schools, or daycare centres due to the proximity between individuals.
It’s essential to follow the proper hygiene precautions to stop the spread of scabies, and it’s vital to maintain adequate hygiene by consistently washing your hands and avoiding sharing personal items such as clothing or towels. Additionally, it’s crucial to treat all affected individuals simultaneously to eliminate the infestation.
By understanding how scabies spread and taking necessary precautions, we can minimize their impact on our lives and protect ourselves from this bothersome condition. Stay informed about its symptoms to ensure early detection and prompt treatment!
Symptoms of Scabies in Humans
–Common Symptoms of Scabies in Humans
Scabies, a highly contagious skin condition, occurs by the microscopic mite Sarcoptes scabiei. Millions of people worldwide are affected by a disease that can cause intense itching and discomfort. Recognizing the symptoms of scabies is crucial for early detection and prompt treatment.
– Most common symptoms of scabies in Humans
One of the most common symptoms of scabies is severe itching, especially at night. The itchiness is often relentless and can cause sleep disturbances, causing daytime weariness and irritation. Another telltale sign is a rash of small red bumps or blisters that may appear in clusters or lines on the skin.
Scabies infestation commonly occurs in areas where there are folds or creases in the skin, such as between fingers, wrists, elbows, armpits, waistline, buttocks, genitals, and breasts (in women). It may affect the head, face, neck, palms, and soles in children and infants.
In some cases, symptoms may take weeks to develop after initial exposure to scabies mites.
You can make it challenging to identify the source of infection. However, the symptoms might appear sooner in individuals with prior exposure (1-4 days).
Note that healthcare providers can easily misdiagnose scabies as other skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis due to their similar appearance.
A physical examination by a medical expert is the most reliable method of confirmation of a diagnosis. During this examination, the professional will check for specific signs, such as female mite burrows. If you suspect you have scabies, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly.
Treatment typically involves topical creams or lotions containing insecticides that kill adult mites and their eggs.
In some cases, a second round of treatment may be necessary.
Prevention measures include avoiding close personal contact with infected individuals, washing clothing, bedding, and towels regularly, and vacuuming living spaces thoroughly. Following these guidelines can help prevent the further spread of this irritating condition.
–Less Common but Possible Symptoms of Scabies Infestation
Scabies, a highly contagious skin infestation caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite, is commonly associated with symptoms such as intense itching and a rash. However, individuals should be aware of some less common but possible symptoms.
– Intense itching at night
One of these less common symptoms is intense itching at night. Scabies mites are nocturnal creatures and their activity increases during nighttime. As a result, individuals may experience heightened itching sensations during this time.
–Sores due to scratching
Another symptom that may occur due to scabies infestation is the development of sores due to scratching. The constant scratching to relieve the itchiness can break the skin’s surface, leading to open sores. These sores become infected if proper hygiene measures are not followed.
– Thick crusts on the skin
In some cases, scabies infestations can lead to the development of thick crusts on the skin. These crusts typically develop when scabies are left untreated for an extended period or when there is a delay in seeking medical attention. The crusts are a result of excessive scratching and skin irritation.
It is important to note that while these symptoms may occur in some cases, they are not always present in every individual with scabies infestation. Suppose you suspect you have scabies or experience any unusual symptoms related to your skin health. Consulting with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options is crucial in that case.
Deeper into the Symptoms of Scabies in Humans
–Nodules and Papules: Understanding Skin Lesions
Scabies doesn’t limit itself to surface-level irritations. It can lead to the formation of nodules and papules, deeper skin lesions that contribute to the overall discomfort. Identifying these manifestations aids in a comprehensive diagnosis.
–Intense Nighttime Itching: A Disturbing Pattern
One peculiar aspect of scabies is the worsening of itching during nighttime. The relentless scratching can disturb sleep patterns, affecting physical and mental well-being. Understanding this pattern is critical to addressing the condition effectively.
Differentiating Scabies from Other Skin Conditions with Similar Symptoms
Differentiating between scabies and other skin conditions with similar symptoms can be challenging, as they may share common characteristics. However, understanding the key differences can help in accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Scabies also is a contagious skin disease caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei. It is characterized by intense itching, particularly at night, along with small burrow-like tracks on the skin. These burrows are often found in areas such as the wrists, elbows, and genital region.
–Eczema
On the other hand, eczema is a chronic inflammatory condition that leads to dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. Unlike scabies, eczema does not involve burrows or mite infestation. It can occur anywhere on the body and is commonly seen in areas such as the face, neck, and flexural folds (inner elbows or behind knees).
–Bed bug bites
Differentiating scabies from bed bug bites can also be challenging due to similar symptoms like itchiness and red bumps. However, bed bug bites usually appear in clusters or linear patterns on exposed body areas, while scabies burrows are more characteristic of scabies infestation.
–Allergic Reaction
Lastly, an allergic reaction may also cause itching and redness of the skin but lacks specific patterns or burrows associated with scabies. Allergic reactions typically occur after exposure to allergens like certain foods or medications.
To accurately differentiate between these conditions, It is critical to see a healthcare practitioner who can thoroughly examine your symptoms and medical history. They may also perform skin scrapings or patch tests for an accurate diagnosis.
Scabies in Different Age Groups
Scabies can affect individuals of all ages, with specific age groups experiencing unique challenges.
– Infants and Children
Infants and children may develop scalp, face, and palm scabies, requiring specialized care and gentle treatment.
Adults and the Elderly
Adults and the elderly may face complications due to existing health conditions, emphasizing the need for prompt and thorough treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
If you suspect that you or someone close to you may have scabies, it is crucial to seek proper diagnosis and treatment. The first step in diagnosing scabies is a physical examination by a healthcare professional. They will carefully examine the affected areas of your skin for signs of the characteristic burrows, blisters, or rash.
Your doctor may conduct a skin scraping test to confirm the diagnosis. During this procedure, they will gently scrape off a small skin sample from an affected area and examine it under a microscope for mites, eggs, or faecal matter.
Once diagnosed with scabies, prompt treatment is essential to prevent the infestation from spreading further. The most common form of therapy involves applying topical creams or lotions prescribed by your healthcare provider directly onto the affected areas.
These medications usually contain permethrin or lindane, killing the mites and their eggs. It’s important to follow your doctor’s instructions on how long to leave the medication on before washing it off.
Doctors may prescribe oral medications if the infestation has spread widely or fails to respond to topical treatments. These medications work systemically throughout your body to eliminate the mites.
It’s also vital to simultaneously treat everyone in close contact with an infected individual, even if they are not showing symptoms yet. It prevents reinfestation and helps eradicate any hidden mites that could later cause reinfection.
Remember, avoiding self-diagnosis and refraining from using over-the-counter treatments is crucial, as they may result in misdiagnosis or inadequate treatment. For an accurate diagnosis and customized treatment suggestions, always consult a doctor.
Prevention Measures
When it comes to scabies, prevention is critical. Here are some measures to protect yourself and others from this contagious skin condition.
– Wash your hands regularly
First and foremost, practice good hygiene. Wash your hands regularly with soap and water, especially after coming into contact with someone with scabies. Avoid sharing personal things like clothing, towels, or bedding with an infected person is advised.
If you suspect that you or someone in your household has scabies, seek prompt medical attention. Treatment and detection at an early stage can help stop the mites from spreading to other people.
– Living environment clean and tidy
Keep your living environment clean and tidy. Vacuum carpets regularly and wash bedding at a high temperature to kill any mites that may be present.
If you have been diagnosed with scabies, follow your doctor’s instructions for treatment diligently. To ensure the eradication of all mites from your body, complete the entire prescribed course of medication.
Inform close contacts about your condition so they can take necessary precautions. It’s better to be safe than sorry when preventing the spread of scabies.
Remember that prevention is not only about protecting yourself but also about safeguarding those around you. By taking these precautions, communities can reduce the chance of scabies transmission within communities and maintain healthy skin for everyone involved.
Understanding the Impact of Scabies on Mental Health
Suffering from scabies may harm both your mental and physical well-being.
The constant itchiness, discomfort, and visible skin rashes can cause aggravation, humiliation, and even shame. These emotional responses are entirely normal, given the challenging nature of this condition.
Scabies can cause significant anxiety and stress due to its highly contagious nature. People may fear spreading the infestation to their loved ones or worry about being ostracized by others due to the stigma associated with scabies. These can result in social isolation and withdrawal from daily activities, leading to feelings of loneliness and depression.
Additionally, sleep disturbances are common among individuals with scabies, as itching tends to worsen at night. Lack of quality sleep can further exacerbate mood disorders and increase irritability during daytime hours.
The impact of scabies on mental health should not be overlooked or dismissed. People with this condition must consult a medical professional for assistance, as they can offer therapeutic and psychological support during recovery.
Remember that you are not alone in dealing with scabies-related mental health challenges. Reach out for help when needed- resources are available to help you manage the disease’s physical symptoms and emotional components.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the Symptoms of Scabies in humans is the first step towards effective management. Each symptom provides valuable insights into the condition, from relentless itching to visible rashes. Remember, seeking professional advice is paramount for accurate diagnosis and timely relief.
Hi there! I’m content writer and blogger. With over two years of experience, I’ve shared my passion for writing across various platforms. I firmly believe in the transformative power of words and look forward to sharing this journey with you. Enjoy my work!