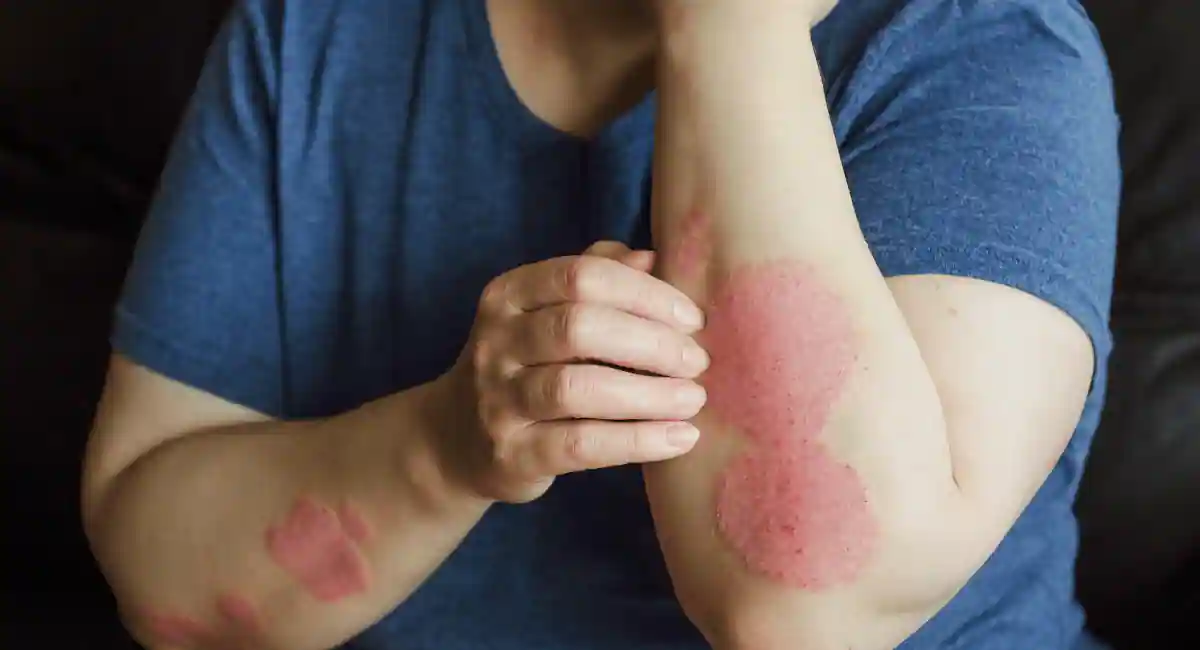
Skin health is a reflection of our body’s internal state and a barrier that constantly interfaces with our environment. There is a delicate interplay between the nutritional value of our diets and the integrity of our skin. The interplay significantly pronounces regarding vitamin deficiencies which can lead to various skin lesions manifesting differently. For medical professionals, health enthusiasts, and dermatology patients seeking more in-depth insights, this post navigates the complex topic of skin lesions caused by vitamin deficiencies to offer clarity, understanding, and actionable steps for healthy skin.
The Impact of Skin Lesions on Your Health
The skin is our body’s biggest organ, protecting us from the external environment. Skin lesions, which are skin surface changes or color, can indicate an underlying condition. They often serve as a visible indicator of our overall health. Understanding the root causes of these lesions can help individuals and healthcare providers take appropriate action, not just for cosmetic reasons but for improving overall well-being.
What Is a Skin Lesion?
A skin lesion is any abnormal change in your skin’s color, texture, or shape. It might vary from a small, hardly visible mark to a more significant, noticeable abnormality. Skin sore can be benign (harmless) or malignant (cancerous). Benign skin lesions are usually harmless, but It is critical to have them examined by a doctor to rule out any more profound problems. Malignant skin lesions, on the other hand, can be severe, necessitating immediate diagnosis and treatment.
How Common are Skin Lesions?
Skin lesions are common, affecting millions of people worldwide. It’s estimated that up to 80% of the population will develop at least one skin lesion during their lifetime. While specific lesions are more common in certain populations or age groups, such as acne in teenagers and skin cancer in older adults, most anyone can develop a skin lesion at some point.
What causes lesions on the skin?
Skin lesions can result from many factors, including infections, allergic reactions, autoimmune disorders, and genetic predispositions. Environmental influences such as UV radiation and chemical exposure also play significant roles in lesion development.
What diseases cause skin lesions?
Several diseases can cause skin sore. Some of the common ones include:
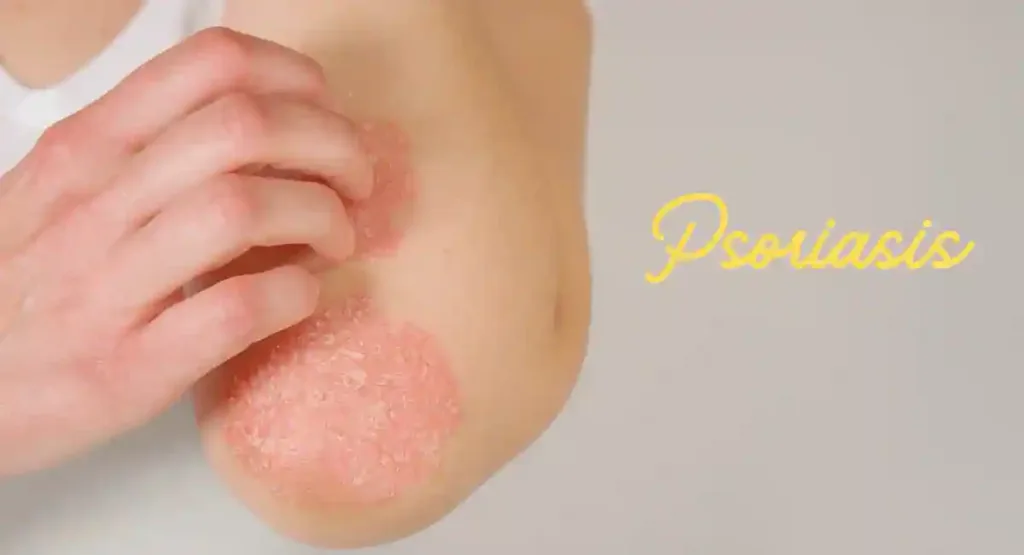
1. Psoriasis:
Psoriasis is a long-term autoimmune disorder leading to red, scaly skin areas. These patches, known as plaques, can be itchy and painful.
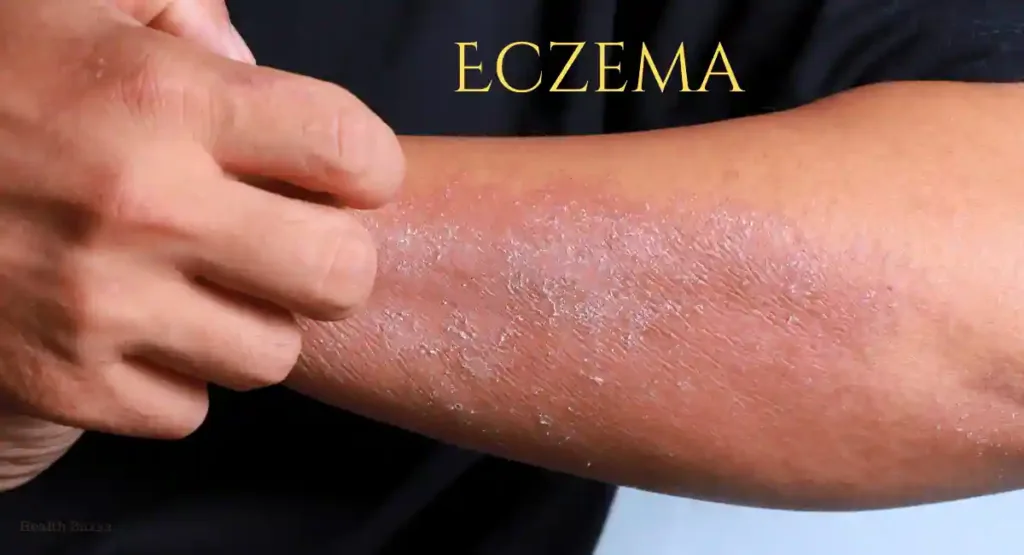
2. Eczema:
Eczema, also called atopic dermatitis, is a condition that causes inflamed, itchy, and red skin. It can lead to skin lesions, including blisters, crusts, or thickened skin.
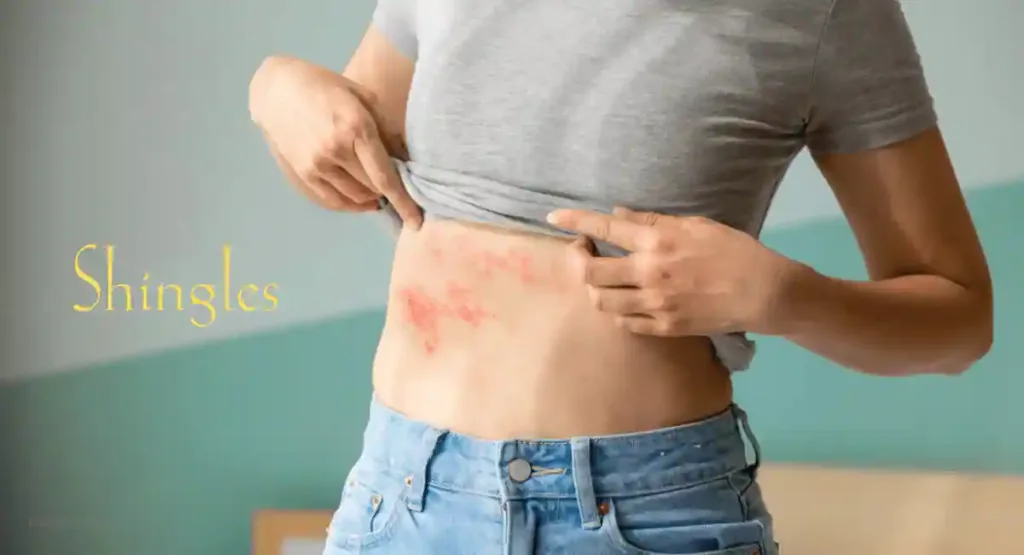
3. Shingles:
The varicella-zoster virus, which causes chickenpox, is the source of shingles. It usually manifests as a painful rash with fluid-filled blisters that develop into crusted lesions.

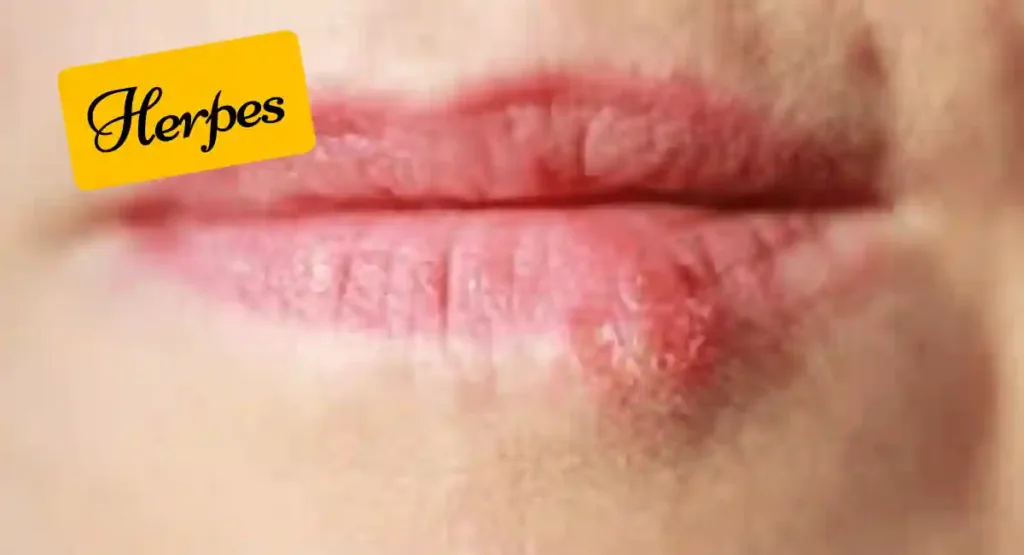
4. Herpes:
A viral infection called herpes can result in skin sores, particularly in the genital area or around the mouth. The lesions are usually small, fluid-filled blisters that can be painful and itchy.
5. Impetigo:
Impetigo is a highly contagious bacterial skin infection primarily affecting children. It causes red sores that quickly rupture, leaving honey-colored crusts or scabs behind.
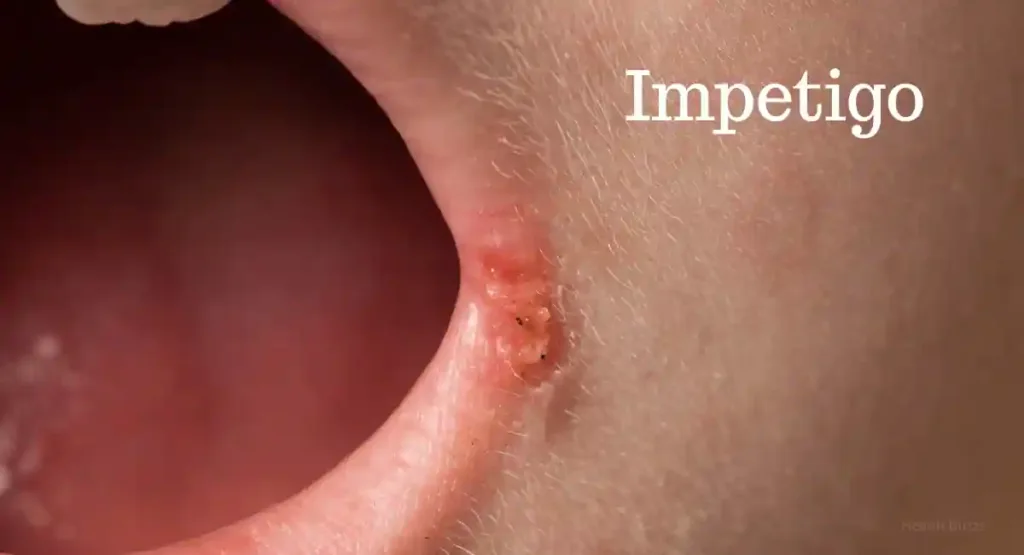
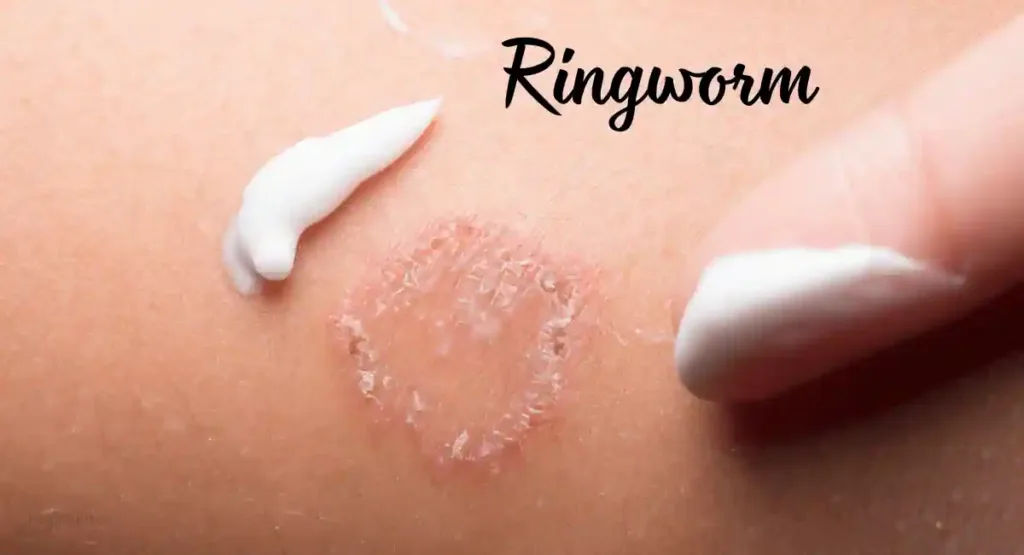
6. Ringworm:
Ringworm is caused by a fungal infection rather than a worm, as the name implies. Usually, it appears as a circular, red rash with raised edges that may cause itching or scaling.
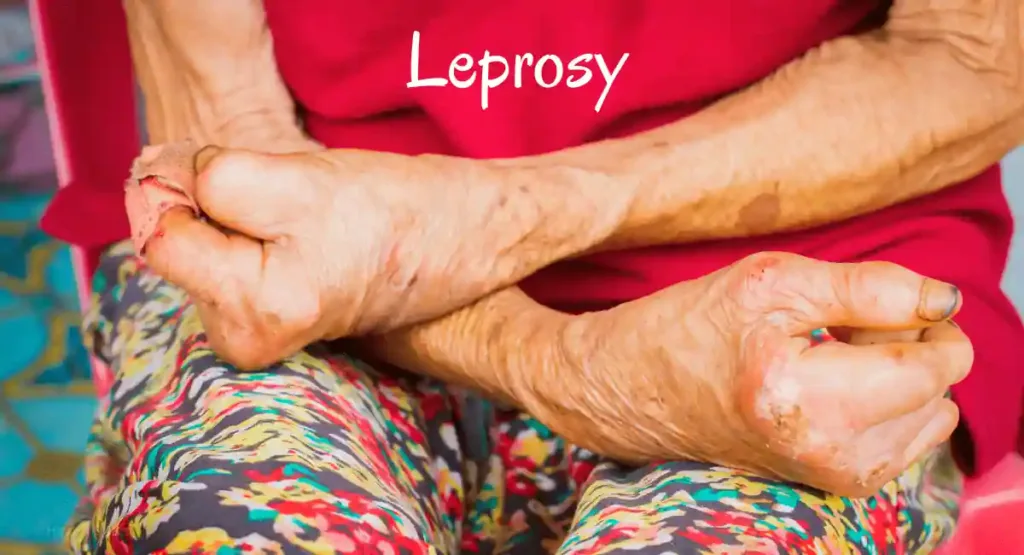
7. Leprosy:
Leprosy, also known as Hansen’s disease, is a chronic infectious illness caused by Mycobacterium leprae. It can cause skin lesions, which may appear as discolored patches or nodules, and usually occur on more relaxed body areas, such as the hands, feet, and face.
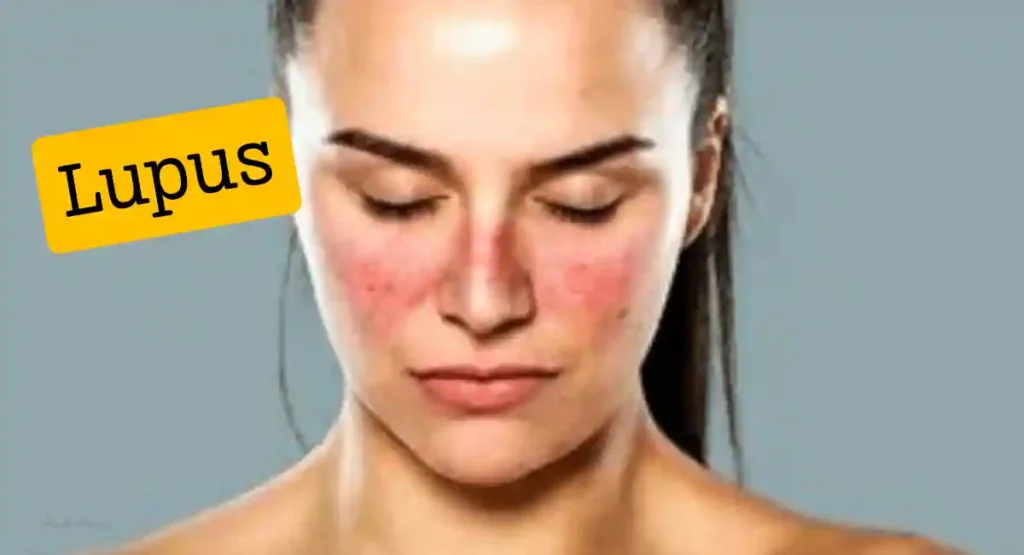
8. Lupus:
Lupus is an autoimmune disease affecting multiple organs, including the skin. It can cause various skin lesions, such as a butterfly-shaped rash on the face, discoid lesions (round, scaly patches), or ulcers.

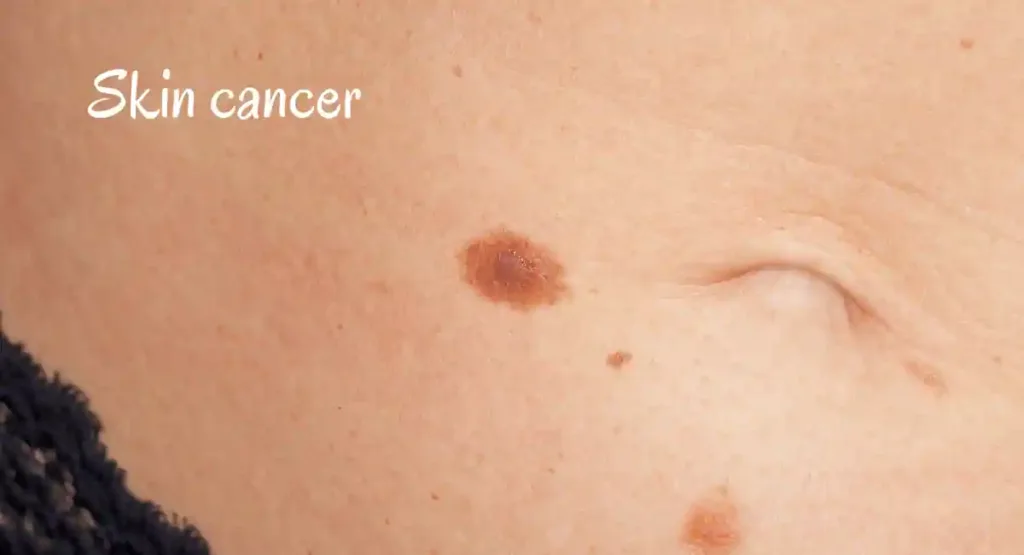
9. Skin cancer:
Skin cancer includes basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma can cause skin lesions. These lesions may manifest as a growing bump, a sore that doesn’t heal, a scaly patch, or an irregularly shaped mole.
It’s worth noting that this isn’t an entire list; many other diseases and conditions can produce skin sores. If you observe any uncommon or troubling skin lesions, you should visit a doctor for a correct diagnosis and treatment.
What are the types of primary skin lesions?
A skin lesion is a broad term for any abnormality manifesting as a rash, mole, blister, bump, or ulcer. The severity and underlying cause of these lesions can vary. Some common types of skin lesions include:
5 types of primary skin lesions
The five types of primary skin lesions are:
- Macules: Small flat spots that can be of different colors
- Papules: Solid raised areas that are less than 1 cm in diameter
- Plaques: Large regions of dull skin
- Nodule: A solid, raised bump located more profoundly in the skin layers than a pimple
- Vesicles: Small, fluid-filled blisters
- Pustules: Blisters filled with pus
These primary lesions can further evolve or combine to form secondary lesions such as crusts, ulcers, or scars, depending on the underlying cause or condition.
What are the types of secondary skin lesions?
5 types of secondary skin lesions
The five types of secondary skin lesions are:
- Crusts: Dried exudate or blood on the skin’s surface, often resulting from serous or purulent fluid drying.
- Scales: The skin may exhibit dry, scaly, or rough patches due to certain skin conditions like psoriasis or eczema.
- Ulcers: Disruption or loss of the epidermis and dermis, often exposing underlying tissue, resulting from trauma, infection, or circulatory issues.
- Fissures: Linear cracks or breaks in the skin, typically occurring in areas prone to dryness or excessive moisture, such as the heels or between the toes.
- Scars: When you get injured or have surgery, your body naturally heals itself by forming fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin. Scars may vary in appearance and texture depending on the severity and type of injury.
Each type of lesion can indicate a different health issue, ranging from benign to severe. Identifying these lesions’ specific characteristics and changes is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
What are the symptoms of skin lesions?
Symptoms of Skin Lesions
Skin lesions can be alarming and may indicate various underlying conditions. Understanding the symptoms associated with skin contusion is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment.
- Infections: Examples of diseases that may cause skin lesions include bacterial, viral, or fungal infections.
- Allergic reactions: Allergic reactions like contact dermatitis or hives can also cause skin lesions.
- Autoimmune diseases: Examples of such conditions could be psoriasis or lupus.
- Skin cancers: Lesions can be precursors to skin cancer or indicate its presence.
- Nutritional deficiencies: Lack of specific vitamins or minerals can manifest as skin sore.
Lesions on the skin refer to areas of abnormal tissue or growth that various factors can cause. They may appear as sores, ulcers, bumps, or skin color or texture changes.
Common Symptoms of Skin Lesions
1. Itching and Irritation
One of the hallmark symptoms of skin lesions is itching and irritation. Affected areas may feel intensely itchy, leading to scratching and further skin damage.
2. Redness and Inflammation
Skin lesions often manifest as areas of redness and inflammation. The affected skin may appear swollen, tender, and warm.
3. Pain and Discomfort
Some skin contusion can be painful, causing discomfort and sensitivity. Pain levels may vary depending on the severity and underlying cause of the lesion.
4. Changes in Skin Texture
Skin lesions can alter the skin’s texture, causing roughness, scaling, or the formation of raised bumps or plaques.
5. Bleeding and Crusting
Sometimes, skin lesions may bleed or develop crusts, especially if scratched or irritated. If you experience continuous bleeding or crusting, it is advisable to seek medical attention.
What vitamin deficiency causes skin lesions?
Vitamin deficiency symptoms on skin
Vitamins are essential nutrients that play a crucial role in maintaining overall health, including the health of our skin. When our bodies lack certain vitamins, it can manifest in various symptoms, some of which become visible on the skin. Understanding these symptoms is vital for identifying potential deficiencies and taking appropriate measures to address them.
Vitamin Deficiencies and Their Role in Skin Lesions
Vitamins are vital components for good health and function of the human body, and Their absence can lead to various health issues, including skin lesions. Understanding how each vitamin affects the skin can illuminate potential deficiencies and how to address them.
1. Vitamin A Deficiency and Skin Lesions
Vitamin A promotes skin health by repairing and maintaining cells. A vitamin insufficiency may cause skin concerns, including:
- Dryness: The skin becomes rough and flaky.
- Hyperkeratosis: The thickness of the skin’s outermost layer is known as hyperkeratosis.
- Keratomalacia: A condition that causes the transparent, glossy surface of the eye’s cornea to turn dry and opaque, leading to blindness.

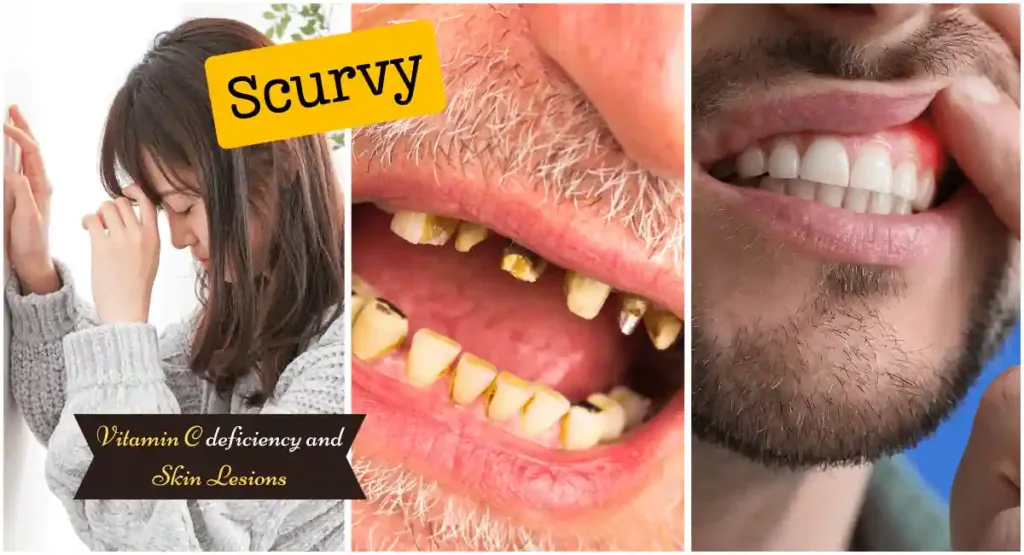
2. Vitamin C Deficiency and Its Impact on Skin Health
Collagen, the protein that provides skin its elasticity, is produced with the help of vitamin C. Without it, skin health can deteriorate, and lesions can develop, such as:
- Scurvy: A disease characterized by weakness, anemia, gum disease, and skin lesions.
- Easy bruising: Due to weakened blood vessel walls.
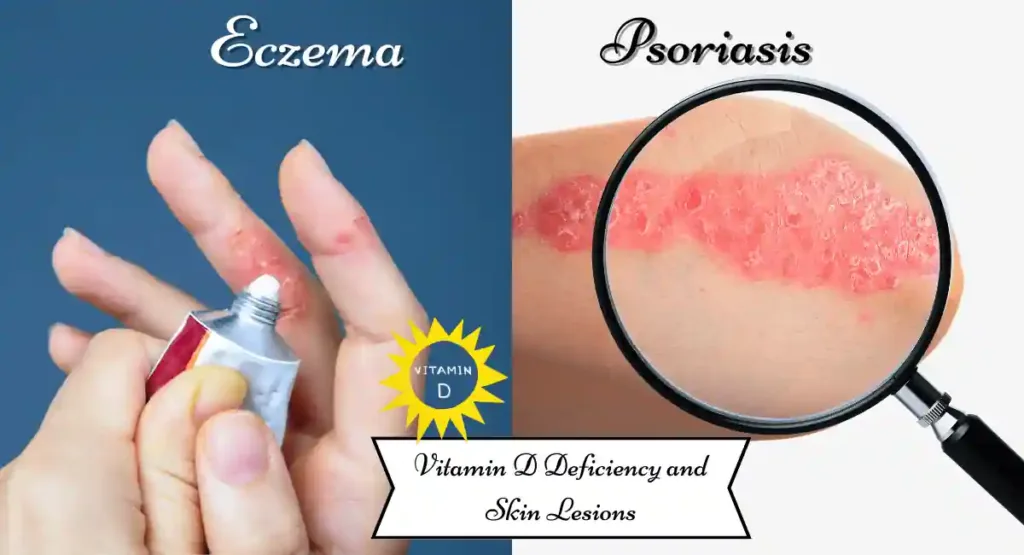
3. Vitamin D Deficiency and the Connection to Skin Lesions
Commonly referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” Skin cell metabolism, development, and healing are all influenced by vitamin D. A deficiency in this vitamin might lead to:
- Psoriasis: A skin disorder characterized by a fast growth of skin cells that results in surface scaling.
- Eczema: A group of conditions that cause the skin to become inflamed or irritated.
Understanding these deficiencies allows for targeted nutritional strategies to help maintain healthy skin.
Other Factors Influencing Skin Lesions
Beyond vitamins, several other aspects of our health and environment can contribute to the development of skin contusion.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to certain chemicals, environmental pollutants, and allergens can cause or exacerbate skin lesion development. For example, contact dermatitis is a common condition triggered by skin contact with a chemical that creates an allergic reaction or irritation to the skin.
Allergies and Sensitivities
Food allergies and intolerances can also result in skin contusion, such as itching, redness, or raised patches on the skin. Identifying and avoiding these triggers is an essential step in maintaining healthy skin.
How Can I Reduce My Risk of Skin Lesions?
Prevention Tips for Skin Lesions
To prevent skin sore and maintain healthy skin, consider the following tips:
• Protect from the sun’s harmful rays: Regularly apply sunscreen, wear protective clothing, and seek shade.
• Avoid skin irritants: Use gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and moisturizers.
• Practice good hygiene: Wash hands thoroughly and avoid sharing personal items with skin, such as towels, razors, or clothing. Seek medical treatment if open wounds or skin conditions exist.
• Limit exposure to harsh chemicals, including hair dyes, nail polish, and hair removal products. Choose gentle, natural alternatives.
• Maintain a healthy diet and active lifestyle: Consuming fruits, vegetables, and consuming whole grains can provide essential nutrients for good skin.
Exercise regularly: Frequent exercise helps lower stress levels and increase blood flow, which can worsen skin disorders.
• Understand benign skin lesions: Understand their prevalence, causes, symptoms, and types. See a dermatologist for evaluation and treatment if skin changes or persistent symptoms occur.
Importance of a Balanced Diet and Nutritional Supplements
The best defense against vitamin shortages and, consequently, skin infections is to ensure that your diet is well-balanced and full of a variety of nutrient-dense foods. For those with conditions that hinder proper nutrient absorption, supplements under the guidance of a healthcare professional can be beneficial.
Dermatological Interventions for Skin contusion
For existing skin contusion, the first step is seeking medical advice. Dermatologists can perform in-depth assessments and provide targeted treatments, such as topical preparations, light therapy, or systemic medications. Professional advice is invaluable in navigating the complex landscape of skin health.
The Role of Vitamin E in Skin Health and Lesion Prevention
Among the many effective antioxidants that have a significant benefit on skin health is vitamin E. Its primary purpose is to shield the skin from damage from oxidation caused by free radicals, which can result in skin diseases and early aging. A deficiency in vitamin E might manifest through symptoms such as:
- Dryness and flaking: This occurs due to the skin’s reduced ability to retain moisture.
- Redness and irritation: A compromised skin barrier can lead to increased sensitivity.
- Impaired wound healing: Vitamin E is critical in the skin’s natural healing process.
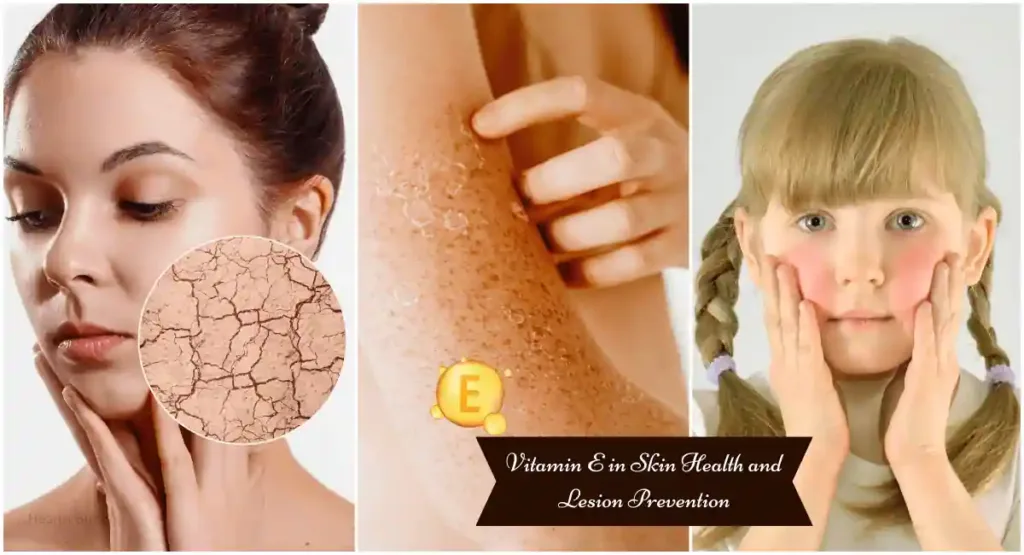

Ensuring an adequate vitamin E intake can reinforce the skin’s barrier function, promote healing of damaged skin, and provide defense against environmental damage. People who consume foods high in nuts, seeds, and leafy green vegetables, as well as those who use supplements carefully, can improve the health of their skin and lower the frequency of skin contusion caused by deficiencies in specific vitamins.
Conclusion:
Your skin’s condition is an indicator of your general health. Because vitamin deficiencies are linked to skin sore, you can take preventative measures to keep your skin healthy. By including a range of nutrients in your diet, being mindful of environmental factors, and seeking professional help when necessary, you can ensure that your skin remains a vibrant, protective, and healthy part of your body.
If you’re experiencing unusual skin changes, consider the possibility of a vitamin deficiency, but remember that self-diagnosis and treatment can be risky. Always seek the advice of a qualified medical professional who can guide you toward the most appropriate and practical solutions. As for dermatology patients, trust the expertise of your healthcare provider and follow the prescribed treatment plan diligently. Your skin is vital to your health, so care for it well.
Hi there! I’m content writer and blogger. With over two years of experience, I’ve shared my passion for writing across various platforms. I firmly believe in the transformative power of words and look forward to sharing this journey with you. Enjoy my work!