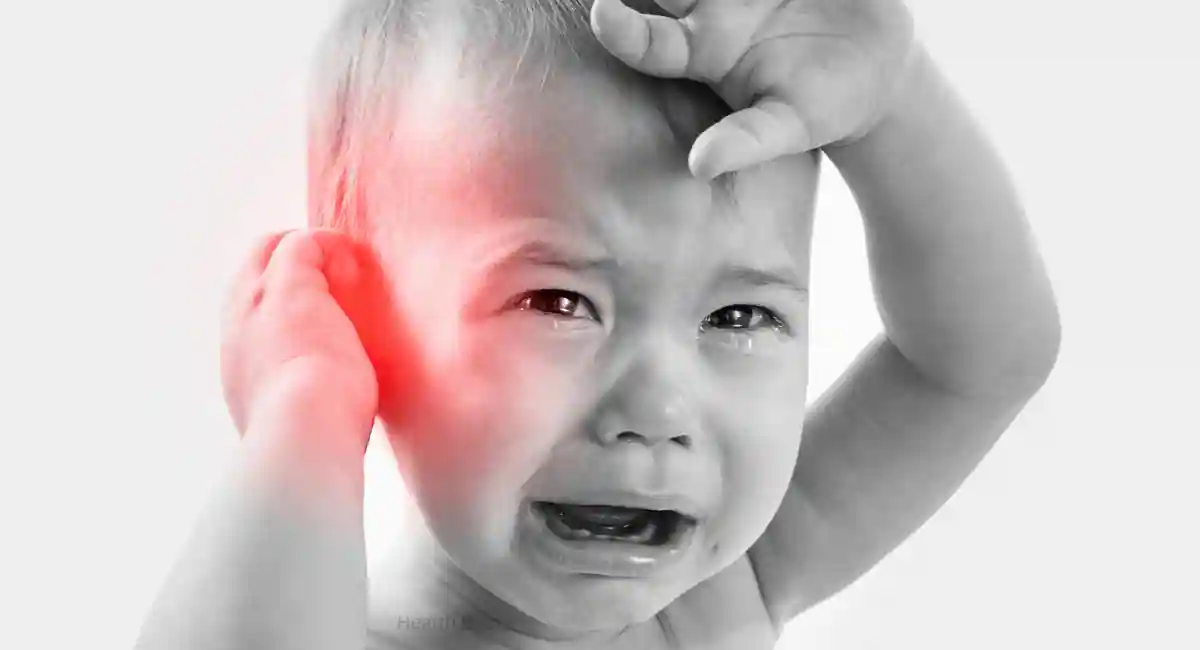
Ear fungal infections, though not as commonly discussed as their bacterial counterparts, can be a source of significant discomfort and even complications if left untreated. Unlike bacteria or viruses, fungi can thrive in various environments, including human ears. In our damp and dark ear canals, a perfect ecosystem exists for some strains of fungus to grow, leading to an ear infection that requires specific care and attention.
Suppose you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of an ear infection, significantly when they differ from the more recognized bacterial variants. In that case, it’s essential to understand the causes, symptoms, treatments, and preventative measures for fungal infections in the ears. Let’s delve deep into the world of ear fungal infections, their diagnosis, and their management to provide comprehensive insight and suggest actionable steps for relief.
Causes and Symptoms of Ear Fungal Infections
Common Causes
Ear fungal infections, also known as otomycosis or swimmer’s ear, are usually caused by the overgrowth of fungi in the ear canal. This overgrowth can be due to various factors:
– Excessive Moisture:
- Waterlogged ears, often resulting from swimming, can create a hospitable environment for fungi to multiply.
– Warmth:
- High temperatures provide favorable conditions for fungi to grow.
– Injury:
- Any damage to the ear canal, like a cut or abrasion, can provide an entry point for fungi.
– Weakened Immune System:
- HIV/AIDS patients and other immune-compromised patients are especially susceptible to fungal infections.
Symptoms to Look Out For
Ear fungal infections can manifest with several telltale signs, including:
1. Itching:
- A robust and persistent itch deep within the ear canal is a common symptom
2. Pain
- usually starts as a mild discomfort but can intensify over time, sometimes accompanied by a headache.
3. Decreased Hearing:
- Due to the blockage in the ear from swelling and infection, patients might experience a reduced ability to hear.
4. Drainage:
- The ear may produce discharge, which can be clear, white, or yellow and may contain particles that resemble mold or mildew.
5. Swelling:
- Redness and swelling inside the ear can indicate an infection.
6. Odor:
- Fungal infections of the ear can sometimes cause a pungent, unpleasant smell.
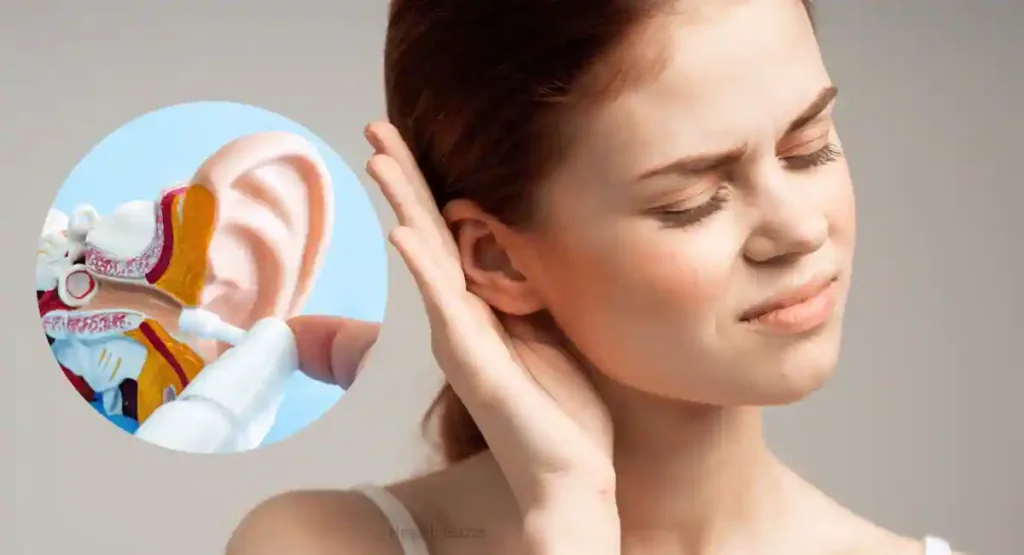
Diagnosis and Medical Treatment
How Ear Fungal Infections Diagnosed
Diagnosing an ear fungal infection requires a medical professional to:
1. Examine the Ear:
- Use an otoscope to look for signs of fungal growth or damage to the ear canal.
2. Collect a Sample:
- A swab might be taken from the ear to be examined under a microscope or sent to a lab to culture the fungi for identification.
Overview of Medical Treatments Available
The treatment of ear fungal infections often involves:
* Antifungal Drops–
Antifungal ear drops are often the treatment of choice if the infection is mild. These medications are usually used for around 1-2 weeks.
* Oral Antifungals–
For more severe cases, may be prescribed to tackle the infection from within.
* Cleaning the Ear–
If there is a significant buildup of fungal debris, your healthcare provider may need to clean your ear canal to help the antifungal medication reach deep into the infection site.
* Steroids–
Sometimes, when there’s significant swelling, you may prescribe steroid drops to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
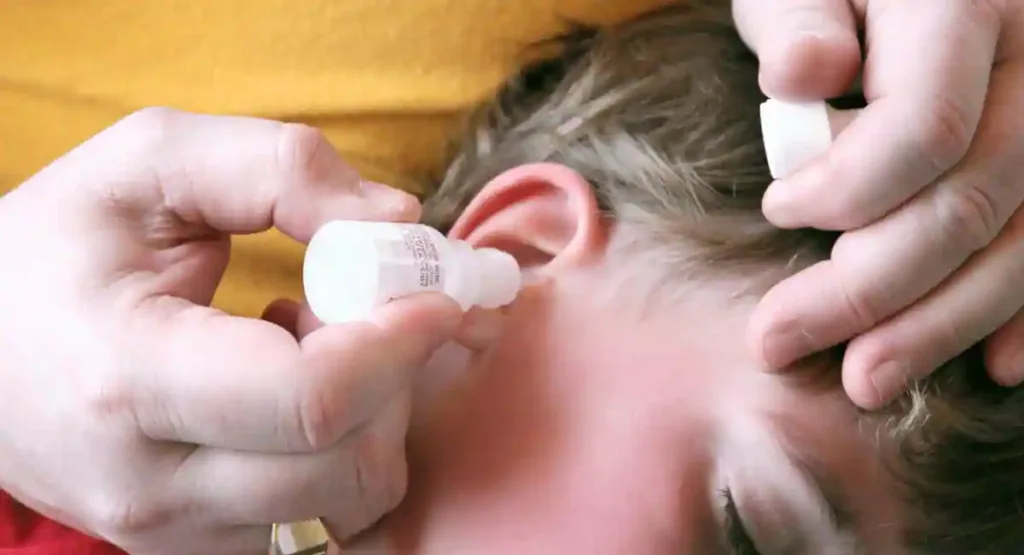
Natural Remedies and Home Care
Alternative Treatments
Several natural and alternative remedies may help alleviate symptoms of a mild ear fungal infection, such as:
1. Vinegar and Alcohol Eardrops–
- A few drops of white vinegar and rubbing alcohol can help dry out the ear and create an inhospitable environment for the fungus.
2. Topical Coconut Oil–
- Some patients have found relief with virgin coconut oil due to its antibacterial and antifungal properties.
Precautions and Self-care Tips
To prevent the spread of the infection or its return, here are some tips:
– Limit Ear Exposure to Water
- Use earplugs or a shower cap when swimming or showering.
– Keep Ears Dry
- Dry your ears thoroughly after water exposure. Tilt your head to each side, and pull on your earlobe in various directions to aid in the water drain.
– Avoid Irritating Substances
- Clear abrasive soaps, shampoos, and ear drops that could further irritate the ear canal.
– Don’t Insert Foreign Objects:
- Cotton swabs or other objects can push fungal spores more profoundly into the ear.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Tips for Preventing Ear Fungal Infections
To minimize your risk of a fungal ear infection, consider:
1. Keeping Ears Clean and Dry:
- Gently dry the outer ear with a towel after bathing or swimming.
2. Disinfecting Earplugs and Headphones:
- Regularly clean any devices that come into contact with your ears.
3. Avoiding Allergens:
- If you are sensitive to specific allergens, manage your exposure to them to reduce the risk of inflammation and, thus, infection.
4. Limiting Ear Canal Trauma:
- If you clean your ears, do so gently. Do not stick any objects into your ear canal.
Complications and When to Seek Medical Help
Complications of Untreated Ear Fungal Infections
Without proper treatment, ear fungal infections can lead to more severe issues, including:
I. Chronic Infection:
- The infection can persist and become more challenging to treat.
II. Spread of Infection:
- Fungal ear infections can spread to the bones of the skull, leading to a condition known as skull base osteomyelitis. It is a rare but severe complication that warrants immediate medical attention.
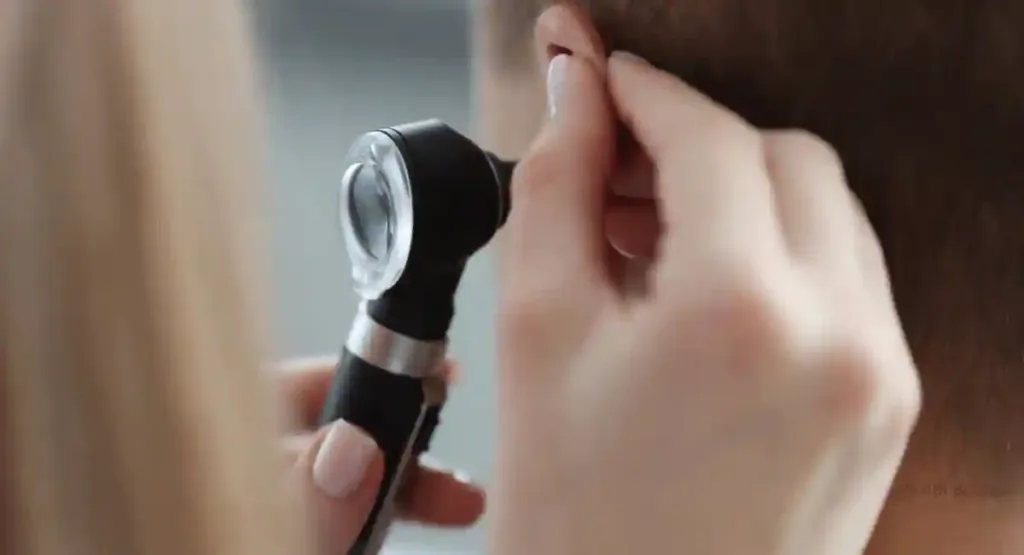

When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
You should seek medical help if you experience:
- Severe pain.
- Signs of hearing loss
- Fluid from the ear, continuous flow, or leakage of
Conclusion
Ear fungal infections are less common but can be as troubling as bacterial ear infections. Understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatment methods gives you more control over how you and your loved ones are shielded from these potentially dangerous illnesses. Be mindful of your ear health whether you opt for conventional treatments, natural remedies, or preventative measures. Always get medical advice from a professional to guarantee an accurate diagnosis and a customized treatment strategy to provide the most effective, safe recovery from an ear fungal infection.
Remember, early detection and treatment are essential. If you suspect you have an ear fungal infection or are unsure about the symptoms you are experiencing, do not hesitate to reach out to a medical professional. With proper care, you can effectively manage ear fungal infections and safeguard your auditory health.
Expert Quotes
2. “Natural remedies can provide relief, but medical treatment is often necessary to completely eradicate the infection.” – Dr. John Smith, General Practitioner
Hi there! I’m content writer and blogger. With over two years of experience, I’ve shared my passion for writing across various platforms. I firmly believe in the transformative power of words and look forward to sharing this journey with you. Enjoy my work!