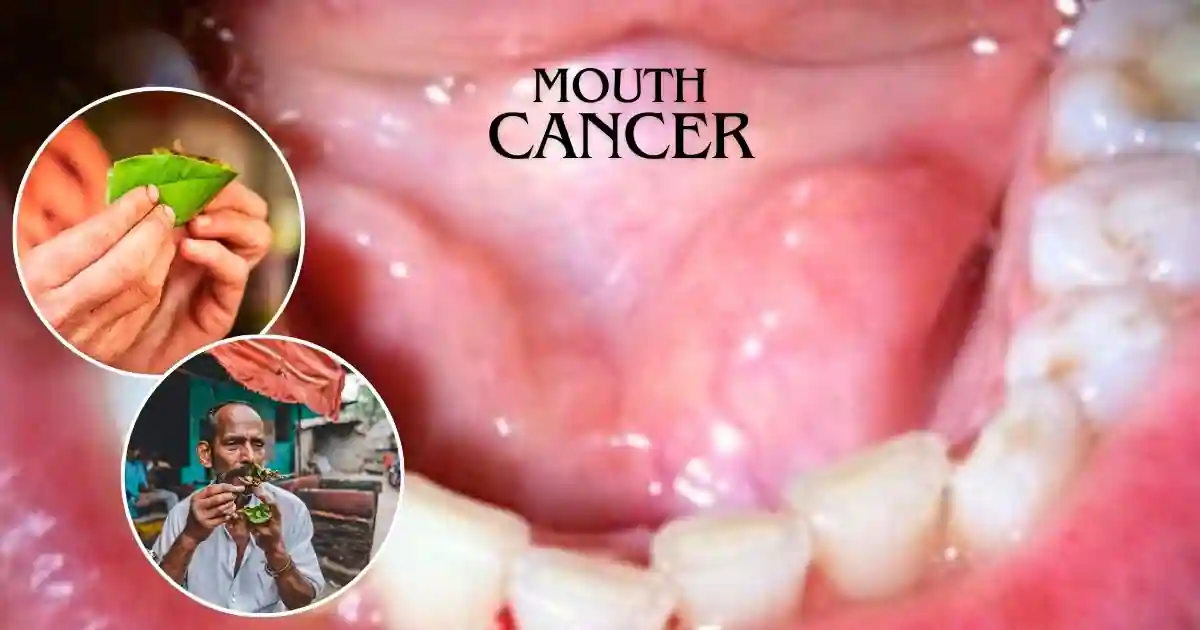
Introduction: Understanding the Link Between Chewing Tobacco and Mouth Cancer
Chewing tobacco is a popular form of smokeless tobacco that has been used for centuries. While it is often perceived as a less harmful alternative to smoking, it is essential to understand the link between chewing tobacco and mouth cancer. This article explores this connection and sheds light on the potential risks and consequences of using chewing tobacco.
What is Chewing Tobacco?
Chewing tobacco, also known as spit or smokeless tobacco, is placed between the cheek and gum or chewed. This form of smoking comes in various shapes and sizes, including loose leaves, plugs, or twists. It is often flavored, giving users a different taste experience. Chewing tobacco contains nicotine, the addictive substance found in cigarettes, which can lead to dependency.
The Link Between Chewing Tobacco and Mouth Cancer
Chewing tobacco poses a significant risk factor for developing mouth cancer. The habit of holding the smoking in the mouth for extended periods exposes the oral tissues to harmful chemicals and carcinogens. These substances can cause cellular changes and DNA damage, ultimately leading to the development of cancer.
Mouth cancer can affect any part of the oral cavity, including the lips, tongue, cheeks, floor or roof of the mouth, and other mucous membrane linings. Chewing tobacco significantly increases the risk of developing mouth cancer, with studies showing that users are at least six times more likely to develop the disease compared to non-users.
Other Health Risks Associated with Chewing Tobacco
Beyond mouth cancer, chewing tobacco is associated with several other health risks. These may include gum and tooth disease, oral leukoplakia (a precancerous condition), pancreatic cancer, and cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes. Additionally, chewing tobacco can lead to nicotine addiction, resulting in dependency and withdrawal symptoms.
Prevention and Quitting
The best way to prevent the development of mouth cancer and other associated health risks is to avoid using chewing tobacco altogether. Quitting can be challenging due to nicotine addiction, but support from healthcare professionals, counseling, and various nicotine replacement therapies, such as patches or gums, can significantly increase the chances of successfully quitting.
Chewing tobacco may seem like a less harmful alternative to smoking, but it is essential to understand the vital link between chewing tobacco and mouth cancer. Individuals can make informed decisions about their tobacco use by recognizing the risks and understanding the potential consequences. Quitting chewing tobacco is the most effective way to reduce the risk of mouth cancer and other associated health problems.
Common Signs of Mouth Cancer Caused by Chewing Tobacco
1. Persistent sores or ulcers:
- One of the most common signs of mouth cancer is the presence of sores or ulcers that do not heal within a few weeks. These sores may be painless in the early stages, making them easy to overlook.
2. Red or white patches:
- Any red or white patches on the gums, tongue, or other areas inside the mouth could indicate mouth cancer. These patches may be slightly raised or have a velvety appearance. These patches may be raised, rough, or irregular in shape.
3. Swelling or lumps:
- Mouth cancer can cause swelling or the development of lumps in the mouth, throat, or neck. These lumps may be painless or may cause discomfort or pain. If you notice a lump or swelling in your mouth, on your tongue, or in the neck area, it is essential to get it checked by a healthcare professional. Although not all lumps are cancerous, we should evaluate them to rule out severe conditions.
4. Chronic lousy breath:
- Chewing tobacco can contribute to chronic bad breath or an unpleasant taste in the mouth that persists despite dental hygiene measures.
5. Difficulty or pain when chewing or swallowing:
- Mouth cancer can challenge chewing or consuming food. You may experience pain or discomfort while trying to eat or drink. Mouth cancer can lead to difficulties or pain when chewing or swallowing food. There may be a feeling of food getting stuck in the throat or frequent choking episodes.
6. Changes in speech:
- Mouth cancer can cause changes in the way you speak. You may notice slurred speech, persistent hoarseness, or difficulty pronouncing certain words.
7. Numbness or tingling:
- In some cases, mouth cancer caused by chewing tobacco can lead to numbness or tingling sensations in the mouth, lips, or tongue. Numbness or a persistent tingling sensation in the mouth, lips, or tongue can be a sign of nerve damage caused by mouth cancer.
8. Loose teeth:
- Mouth cancer can affect the stability of your teeth, causing them to become loose or fall out unexpectedly.
9. Ear pain:
- Mouth cancer can cause referred pain to the ears, resulting in persistent earaches or discomfort.
10. Changes in voice:
- Chewing tobacco-related mouth cancer can affect the vocal cords or surrounding areas, leading to changes in the voice, such as hoarseness or a raspy voice.
11. Unexplained weight loss:
- In advanced stages of mouth cancer, unexplained weight loss may occur due to difficulties in eating and the body’s increased energy requirement to fight the disease.
12. Difficulty wearing dentures:
- If you wear dentures and suddenly find it difficult to keep them in place or experience discomfort while wearing them, it could be a sign of mouth cancer.
It is important to note that other conditions can also cause these signs and symptoms, so it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. Early detection of mouth cancer significantly increases the chances of successful treatment and recovery. If you are using chewing tobacco or other forms of smokeless tobacco, quitting can dramatically reduce your risk of developing mouth cancer.
How many types of mouth cancer
There are several types of oral cancer in English. These include:
1. Squamous cell carcinoma–
This is the most common type, accounting for about 90% of oral cancer cases. It typically starts in the thin, flat cells that line the lips and oral cavity.
2. Verrucous carcinoma–
This is a less aggressive form of oral cancer that usually develops on the gums, floor of the mouth, or inner cheeks.
3. Minor salivary gland carcinomas-
These cancers develop in the minor salivary glands throughout the oral cavity.
4. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma-
This is a type of cancer that can develop in various parts of the oral cavity, including the tongue, palate, and floor of the mouth.
5. Adenoid cystic carcinoma-
This rare but aggressive form of oral cancer usually occurs in the minor salivary glands.
6. Acinic cell carcinoma-
This type of oral cancer typically arises in the salivary glands and can affect the mouth or throat.
7. Spindle cell carcinoma-
This rare oral cancer primarily affects the tongue.
8. Basal cell carcinoma-
Although more commonly found on the skin, basal cell carcinoma can also occur on the lips or in the oral cavity.
It is important to note that these are just a few examples, and there may be other less common types of oral cancer as well. A medical professional should always consult for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
The Importance of Early Detection and Seeking Medical Attention
Early detection and seeking medical attention are of paramount importance when it comes to maintaining good health. It plays a crucial role in preventing the progression of diseases, enabling prompt treatment, and improving overall outcomes. Here are some reasons why we should prioritize early detection and seeking medical attention :
1. Timely diagnosis
Early detection allows for the timely diagnosis of various conditions, including chronic diseases such as cancer, diabetes, heart disease, and hypertension. Detecting these conditions early increases the chances of successful treatment and improves long-term prognosis.
2. Preventive interventions
Regular medical check-ups and screenings can help identify potential health risks before they manifest as severe problems. It allows healthcare professionals to provide preventive interventions and lifestyle modifications to mitigate the development of diseases or their complications.
3. Lower treatment costs
Detecting and treating a health condition in its early stages is often less expensive than treating advanced diseases. Early detection reduces medical expenses and prevents the need for complicated and costly procedures.
4. Improved treatment outcomes
With early detection, treatment can be initiated at an earlier stage, often leading to more effective outcomes. Many diseases, such as cancer, are more likely to be successfully treated when diagnosed early.
5. Preventing disease progression
Some diseases, if left untreated, can progress rapidly, leading to irreversible damage or complications. Early detection can help prevent the progression of diseases, improve overall health, and preserve the quality of life.
6. Health education and awareness
Seeking medical attention allows individuals to receive vital health information and education from qualified professionals. It increases awareness about disease prevention, symptom recognition, and the importance of regular screenings, ultimately promoting a healthier lifestyle.
7. Emotional support
Seeking medical attention early can also provide emotional support during challenging times. Healthcare providers can offer counseling and guidance to patients, helping them cope with their condition and make informed decisions regarding their health.
In conclusion, early detection and seeking medical attention are crucial steps in maintaining good health. Regular check-ups, screenings, and prompt medical consultations can lead to early diagnosis, preventive interventions, lower treatment costs, improved outcomes, disease prevention, and emotional support. Prioritizing these actions can contribute to overall well-being and a better quality of life.
Tips for Preventing Mouth Cancer from Chewing Tobacco Use
1. Quit chewing tobacco
- The best way to prevent mouth cancer from chewing tobacco use is to stop using it altogether. Quitting can be challenging, but there are numerous resources available, such as support groups, medications, and counseling services, that can assist in the quitting process.
2. Maintain good oral hygiene
- Brush your teeth twice daily using fluoride toothpaste and floss daily. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings can also help detect any early signs of oral cancer.
3. Stay aware of oral changes
- Regularly check your mouth for any unusual changes, such as persistent sores, white or red patches, lumps, or a sore throat. Consult a dentist or doctor immediately if you notice any ongoing changes or symptoms.
4. Avoid alcohol and tobacco combination
- The combination of alcohol and chewing tobacco increases the risk of mouth cancer exponentially. It is advisable to avoid consuming alcohol while using chewing tobacco.
5. Eat a healthy diet
- A well-balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables provides essential antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals to help reduce the risk of mouth cancer. Add plenty of fresh produce to your meals and limit processed and fatty foods.
6. Protect yourself from the sun
- Prolonged sun exposure can increase the risk of lip cancer. Protect your lips by wearing a wide-brimmed hat, using lip balm with sun protection factor (SPF), or seeking shade during peak sun hours.
7. Educate yourself-
- Learn about the dangers of chewing tobacco, the signs and symptoms of mouth cancer, and the importance of early detection. Knowledge and awareness play a crucial role in preventing and addressing oral cancer.
8. Encourage others to quit-
Support friends and family members who use chewing tobacco to finish. A supportive and understanding environment can significantly assist their journey towards a tobacco-free life.
Remember, prevention is always better than treatment. By following these tips and making positive lifestyle changes, you can reduce your risk of developing mouth cancer associated with chewing tobacco use.
Treatment Options for Mouth Cancer
Mouth cancer refers to developing malignant tumors in the oral cavity, including the mouth’s lips, tongue, gums, cheeks, and roof or floor. Treatment options for mouth cancer can vary depending on the stage and location of the tumor, as well as the overall health of the patient. Here are some standard treatment options:
1. Surgery
Surgery is often the first step in treating mouth cancer. It involves the removal of tumours and affected tissues through surgical procedures. Surgery aims to remove the tumour while minimizing the impact on the surrounding healthy tissues.This involves removing the tumor and nearby tissues. Surgical options may include excision of the tumor, tumor resection, or removal of lymph nodes if cancer has spread.
2. Radiation therapy- Using high-energy radiation to destroy cancer cells
High-energy radiation is directed at the tumor to destroy cancer cells. It can be used alone or in combination with surgery. Radiation therapy is another standard treatment modality for mouth cancer. It uses high-energy radiation to destroy cancer cells. Radiation therapy can be delivered externally, through a machine outside of the body, or internally, through the placement of radioactive sources inside the body.
3. Chemotherapy
Anti-cancer drugs kill or prevent cancer cells from multiplying. Chemotherapy may be used before or after surgery or in combination with radiation therapy. Chemotherapy is the use of drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body. It is typically reserved for more advanced mouth cancers or those that have spread beyond the mouth. Chemotherapy is often used in combination with radiation therapy to enhance its effects.
4. Targeted therapy
This treatment option uses drugs targeting cancer cells, inhibiting their growth and spread.
5. Immunotherapy
These therapies enhance the body’s immune response to fight cancer cells.
Chewing tobacco users should understand the importance of early detection and regular dental check-ups for mouth cancer. By prioritizing these appointments, chewing tobacco users can significantly increase the likelihood of detecting mouth cancer in its early stages and improving their overall prognosis.
Conclusion: Take Action and Protect Your Oral Health
Taking action and prioritizing oral health is essential to maintaining a healthy mouth and overall well-being. You can effectively protect your oral health by following a proper oral hygiene routine, including brushing and flossing regularly, visiting the dentist for regular check-ups and cleanings, and making a healthy oral hygiene routine. Neglecting oral health can lead to dental issues, such as tooth decay, gum disease, and even tooth loss. Additionally, poor oral health has been linked to other systemic diseases like heart disease and diabetes. Therefore, taking action and making oral health a priority in your life is crucial. Doing so can ensure a bright and healthy smile for years to come.
Hi there! I’m content writer and blogger. With over two years of experience, I’ve shared my passion for writing across various platforms. I firmly believe in the transformative power of words and look forward to sharing this journey with you. Enjoy my work!