Diabetes is a long-term medical disorder where the body produces cannot properly regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels. People with diabetes either do not produce enough insulin (a hormone that helps control blood sugar levels) or cannot appropriately use the insulin their body has. It can lead to high levels of glucose in the blood, which can cause a range of health problems if left unchecked.
Types Of Diabetic-
There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2.
Type 1 diabetes-
Insulin-dependent diabetes, or type 1 diabetes, is an autoimmune condition in which the body’s immune system targets and kills the cells in the pancreas that create insulin. To control their blood sugar levels, patients with type 1 diabetes must receive insulin injections or utilize an insulin pump because they do not make any insulin. Typically, children and young adults with type 1 diabetes are diagnosed with it.
Type 2 diabetes-
Type 2 diabetes, also known as non-insulin-dependent diabetes, is the most common form of diabetes. It occurs when the body does not use insulin properly or can not make enough insulin to meet its needs. It is called insulin resistance. Type 2 diabetes is often linked to obesity and a sedentary lifestyle and is more common in older adults, but it is also becoming more common in younger people.
If left untreated, both types of diabetes can lead to serious health problems such as heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and blindness. However, many people with diabetes can lead healthy lives with careful control. It often involves regular blood sugar testing, nutritious food, regular exercise, and occasionally prescription drugs or insulin injections.

7 Diseases You Didn’t Know Were Linked to Diabetes-
Although diabetes is one of the most prevalent medical conditions in America, you may not be aware that it also puts you in danger for several other conditions. Here is a list of seven diseases you may not be aware of related to diabetes.
1) Alzheimer’s disease-
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive brain disorder that gradually destroys memory and thinking skills. It gets worse over time, and eventually, someone with Alzheimer’s may not even be able to recognize family members or understand what they are saying. Studies have shown that people with diabetes have an increased risk of developing Alzheimer’s.
Following more than 18,000 patients for six years, researchers discovered that individuals with diabetes had a 50% higher risk of dementia than those without it. It’s not essentially clear why these two people are connected. But this may be because insulin can cause more damage to nerve cells, which is one cause of Alzheimer’s. Another possible explanation is that high blood sugar levels cause excess free radicals, which the body produces as this interaction between oxygen and glucose. A third theory is that diabetic neuropathy (nerve damage) can cause foot ulcers that can lead to infection.
Those infections can then travel from the leg to the brain and increase the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Type 2 diabetes also increases your chances of macular degeneration, a common eye condition that causes blindness. Other complications include osteoarthritis, heart disease, stroke, and kidney problems. It’s important to remember that you don’t need to get through all of these complications before taking action! Eating healthy and being active will help you stay healthy now and reduce some of the risks later.
2) Cancer-
Diabetes is the leading cause of new cases of blindness among adults aged 20 or older and increases the risk for certain types of cancer, such as pancreatic cancer. People with diabetes are two times more likely to develop cancer. Individuals with type 1 diabetes have a fivefold increase in the incidence of all cancers combined compared to individuals without diabetes. And those with type 2 diabetes have an increased risk of developing cancer as well: one in ten types 2 diabetics will develop some form of it over their lifetime.
People who are at high risk for diabetes should get screened annually. Other health problems that might lead to cancer: The insulin resistance that often accompanies type 2 diabetes can affect the body’s ability to fight infections and control inflammation, which may make you susceptible to colorectal cancer, liver cancer, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. Even though doctors don’t know why this happens, obesity seems to play a part. As if type 2 diabetes wasn’t bad enough on its own!
A study found that women with gestational diabetes were almost six times more likely to be diagnosed with breast cancer than women without the condition. Those with pre-existing diabetes also have higher breast cancer rates, even when they don’t have gestational diabetes.
Check out for these warning signals from your feet, in addition to making sure your cholesterol levels are normal: changes in form, numbness, sores that won’t heal, redness or scaling between toes, and pebbly skin (skin between toes crinkled up like crepe paper). Watch out for the warning symptoms of high cholesterol in your feet, such as changes in form, numbness, sores that won’t heal, redness or scaling between toes, and pebbly skin (skin between toes crinkled up like crepe paper). If any of these sound familiar, see your doctor right away. Early diagnosis makes treating many diseases easier and less expensive, so you’ll be glad you did.
3) Depression-
Depression is a mental illness that not only changes how you feel but can also change the way you think and behave. It may cause distress, sadness, anger, or irritability. Depression can lead to suicide. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that more than 300 million individuals worldwide suffer from depression. 10% of these instances are said to be type 2, diabetes patients.
In one study conducted by the WHO, people with type 2 diabetes had an increased risk of developing depression at any time point during their disease. A review from 2006 found that patients with type 2 diabetes have a four-fold increase in their risk for developing major depressive disorder and an eight-fold rise for developing bipolar disorder. A 2002 study showed that people with diabetes were more likely to experience mood disorders like anxiety and phobias, though they were less likely to experience a generalized anxiety disorder. It’s essential for anyone with a mood disorder to seek help from their physician.
A 2013 study on adolescents showed that many young adults do not know the connection between diabetes and depression. Without proper education, youth can develop mental health problems such as depression without knowing what caused them. What should we do? Mental health experts recommend educating children about the link between diabetes and mood disorders and encouraging them to care for themselves mentally and physically. Adults must talk openly about their feelings and see a therapist if needed. There are even groups specifically for those with diabetes, which focus on wellness and support. You don’t have to fight depression by yourself!
4) Heart Disease-
Heart disease is one of the most common causes of death in people with diabetes. People with diabetes are more likely to have hardening and narrowing of the arteries, also called atherosclerosis. A heart attack or stroke may result. People with diabetes also may have an increased risk for high blood pressure, obesity, high cholesterol and triglycerides, and low HDL (good) cholesterol levels. The risk of heart disease increases with each of these factors. About 20% of people with diabetes will die from heart disease, as opposed to 4% of those without it.
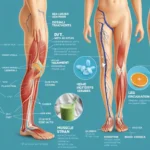
Respiratory Disorders: When your blood sugar level is high, your body tries to remove it by removing water from your cells and putting it in your bloodstream, where the kidneys filter it.
The kidneys may be unable to keep up with this extra load, leading to dehydration and kidney failure. These problems often result in breathing difficulties, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD). Other respiratory diseases may include sleep apnea, asthma, pneumonia, and tuberculosis.
Kidney Disease: People with diabetes are at a higher risk for developing kidney diseases because of high blood sugar. There are two major diabetic kidney diseases: diabetic nephropathy and diabetic retinopathy. Diabetic Nephropathy – When you have diabetes, your blood glucose stays high over time. High blood glucose damages the delicate tissues inside your kidneys, leading to protein leaking into the urine and forming larger clumps called albuminuria. Diabetic Retinopathy – After years of untreated high blood sugar, damage to small blood vessels in the retina can cause them to leak fluid, swell and even close off together, leading to vision loss.
Diabetes may be related to 7 different diseases. If you or someone you know has been experiencing symptoms associated with any of the conditions mentioned earlier, consult a medical professional immediately. Diabetes is manageable but should never go untreated. Take care of yourself and check on others too!
5) Kidney Disease-
If you have diabetes, your body can’t properly break down sugars, which means glucose builds up in your blood instead of being used for energy. One consequence is that excess sugar leads to high uric acid levels in the blood. High uric acid levels make it difficult for your kidneys to do their job: filtering out waste products from the blood and balancing salt in the body. It can lead to a buildup of acids like phosphoric and sulfuric acid in the kidney, eventually damaging them. The resulting kidney disease often progresses quickly and may lead to dialysis or death.
Another complication is that some people with chronic kidney disease might not experience symptoms until they develop an infection or bleed internally. Heart Disease: Having uncontrolled diabetes also increases the risk of heart disease by changing cholesterol, fat, and other substances (lipids) that contribute to plaque buildup on artery walls. That plaque narrows arteries and restricts blood flow, putting strain on the heart. When this occurs, the organ has to work harder and becomes damaged over time.
In addition, high blood sugar amounts can cause proteins called albumin to leak into urine and sodium excretion. These proteins are vital for maintaining proper fluid balance in tissues throughout the body; when too many leaks into the urine, fluids accumulate around organs such as the liver and heart, causing swelling (also known as edema). Over time this condition causes permanent damage that makes these organs less efficient at their jobs. Kidney failure, heart attack, and stroke all become more likely.
Sleep Apnea: Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder where breathing stops for short periods during sleep because airway muscles relax during sleep. It affects about 10% of adults and one-third of children with type 1 diabetes. Often people with sleep apnea don’t know they have it because it’s undiagnosed or goes unnoticed without testing while asleep. Symptoms include loud snoring and pauses in breath followed by gasping or choking sounds. It’s essential to get tested for sleep apnea if you have diabetes because it often uses devices such as CPAP machines (a machine that provides continuous positive airway pressure).
6) Stroke-
In addition to being linked to diabetes, the stroke itself is twice as common in people with diabetes itself. Studies have shown people with the condition to experience a stroke. It’s not clear why this happens. Some experts believe it may be due partly to the effects of high blood sugar on blood vessels, while others think high insulin levels may increase the risk of a clot forming in the brain. Whatever the reason, it pays to know your risks and take steps to lower them.
Most importantly, controlling your blood sugar levels can help prevent or delay many problems with diabetes, such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
Treating Type 2 diabetes isn’t always easy, but getting your health back on track, can reduce your risk for many long-term complications related to the disease. Make sure to talk with your doctor about what lifestyle changes you can make and work towards these goals one at a time. There is no quick fix for diabetes, so changing your life will take some time. The end goal should be healthier living and wellness – not just managing the symptoms.
7) Vision Impairment
Research shows that people with diabetes are at an increased risk of developing a range of eye-related health problems, including cataracts, glaucoma, and diabetic retinopathy. The long-term use of several diabetic drugs can potentially result in vision impairment. Diabetic retinopathy is damage to the retina or tissue in the rear of your eye that is sensitive to light. Depending on the nature, location, and severity of the illness.
There are many therapies available. Diabetic macular edema (DME) is a complication of diabetes in which fluid builds up in front of your retina. People with diabetes who have had the disease for more than 10- years, in addition to people with high blood pressure or high cholesterol levels, are more likely to get it. Other eye conditions include:
- Iritis (inflammation inside the eyeball).
- Vitreous hemorrhage (bleeding into the jelly-like substance behind the lens).
- Diabetic cataract (clouding of the lens).
If you’re experiencing any vision changes, such as blurry vision, difficulty reading, colored spots before your eyes, or difficulty seeing at night, contact your doctor right away.
10- early signs of diabetes-
Diabetes is a chronic disease that interferes with the body’s ability to process blood sugar (glucose). The body’s primary energy source is a form of sugar called glucose. The pancreas’ hormone insulin aids in controlling the amount of glucose in the blood. What are the signs of being diabetic?
Here are ten early signs of diabetes that you should be aware of:
Increased thirst: You may experience increased appetite as the body tries to eliminate excess blood sugar.
Frequent urination: As your body gets rid of excess sugar in your urine, you may need to use the bathroom more often.
Fatigue: High blood sugar levels can cause fatigue and make you tired, even after a whole night’s sleep.
Blurred vision: High blood sugar levels can affect the eye’s lens and cause temporary vision changes.
Slow healing: High blood sugar levels can slow the healing process and increase the risk of infection.
Hunger: Even if you’re eating enough, high blood sugar levels can make you feel hungry because your cells aren’t getting energy from the glucose in your blood.
Dry mouth and skin: High blood sugar levels can lead to dry mouth and skin.
Hands and foots tingling or feeling numb: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves, resulting in numbness or tingling in the hands and feet.
Yeast Infections: Women with diabetes may be more prone to yeast infections.
Mood changes: High blood sugar levels can affect your mood and lead to irritability, anxiety, or depression.
You must talk to your healthcare provider if you notice these symptoms. They can check your blood sugar levels and determine whether you have diabetes or prediabetes, a condition in which blood sugar levels are higher than usual but not too high. To diagnose diabetes early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent the development of more severe complications.
Hi there! I’m content writer and blogger. With over two years of experience, I’ve shared my passion for writing across various platforms. I firmly believe in the transformative power of words and look forward to sharing this journey with you. Enjoy my work!